The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming our world, powering everything from our smartphones to self-driving cars. But this technological revolution comes at a cost. Recent data reveals a significant increase in electricity consumption in the US, partly attributed to the booming AI industry. This raises critical questions about AI’s environmental impact and the urgent need for sustainable solutions.
While the exact figures are still being debated, the correlation between increased AI usage and higher energy consumption is undeniable. This blog post delves into the complexities of AI’s energy footprint, examining the current situation and exploring potential solutions to mitigate its environmental consequences.
The Surge in Energy Demand 📈
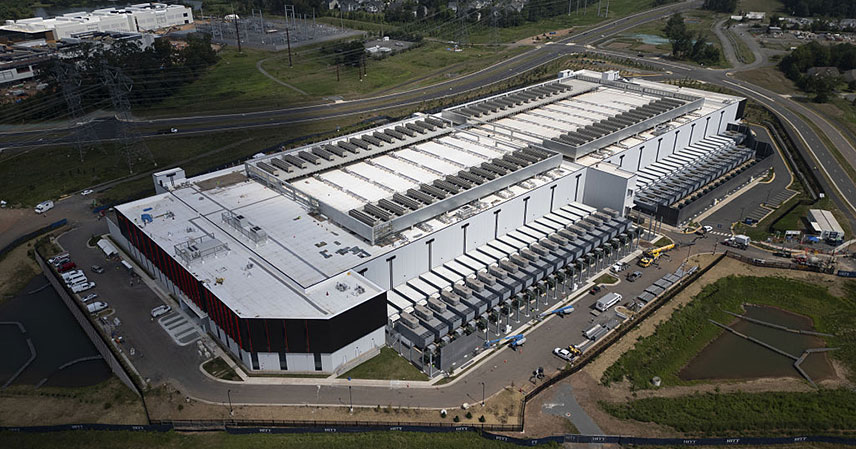
Electricity consumption in the US has seen a notable jump of nearly 4 percent this year compared to the previous year. This increase follows decades of relatively stable energy use. A significant driver of this surge is the rapid expansion of data centers, many of which are dedicated to supporting the growing demands of AI applications. The processing power required for AI algorithms, especially large language models and machine learning, is incredibly energy-intensive.
This increased demand has led to a concerning trend: a rise in the use of coal to generate electricity. As of May, coal’s contribution to power generation is up approximately 20 percent year-on-year. This reliance on fossil fuels significantly undermines efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, highlighting the urgent need for a more sustainable approach to AI development and deployment.
The Difficulty of Accurate Measurement 🧮
Accurately quantifying AI’s energy consumption presents a significant challenge. While researchers can assess the power requirements of individual AI models in controlled environments, translating these findings to real-world scenarios is difficult. Factors such as hardware usage rates, query frequency, and data center efficiency vary considerably, making precise estimations complex.
The lack of readily available, granular data from data centers further complicates the situation. Access to detailed operational information is often restricted, hindering comprehensive assessments of the overall energy footprint of AI systems.
Google’s Insights: A Glimpse into the Future 👀
Google, with its vast data resources derived from real-world applications, offers a unique perspective on AI’s energy impact. Their recent analysis provides valuable insights, revealing that the energy required for a single search has decreased dramatically—by a factor of 33—in just the past year. This demonstrates the potential for significant improvements in energy efficiency through technological advancements and optimization.
However, this progress shouldn’t overshadow the overall challenge. While individual improvements are encouraging, the ever-increasing scale of AI deployments means that even small gains in efficiency might not offset the overall growth in energy demand. Therefore, a multi-pronged approach is necessary to address this issue effectively.
Addressing the Environmental Impact 🌍
The environmental consequences of AI’s energy hunger are substantial and cannot be ignored. The increased reliance on fossil fuels contributes directly to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change. Furthermore, the manufacturing and disposal of AI hardware also carry environmental burdens, including the extraction of rare earth minerals and the generation of electronic waste.
Sustainable practices are crucial. This includes investing in renewable energy sources to power data centers, developing more energy-efficient AI algorithms, and promoting responsible hardware lifecycle management. Collaboration between researchers, industry leaders, and policymakers is essential to navigate this complex challenge.
Key Takeaways 🔑
- AI’s rapid growth is significantly increasing global energy consumption.
- The reliance on fossil fuels to power AI infrastructure is concerning for the environment.
- Accurate measurement of AI’s energy footprint is challenging due to data limitations.
- Technological advancements can improve energy efficiency, as demonstrated by Google’s findings.
- Sustainable practices and collaborations are critical to mitigating AI’s environmental impact.
In conclusion, the energy implications of AI are a complex and evolving issue. While technological advancements offer hope for efficiency, a concerted effort is required to ensure that the benefits of powerful new models like OpenAI’s GPT-5 are not overshadowed by their environmental costs. The future of AI depends on our ability to develop and deploy it in a sustainable and responsible manner.
Source: Google says it dropped the energy cost of AI queries by 33x in one year